门面模式简介
门面模式是对象的结构模式,外部与一个子系统的通信必须通过一个统一的门面对象进行。门面模式提供一个高层次的接口,使得子系统更易于使用。
举个例子,
病人去医院看病,如果把医院作为一个子系统,按照部门职能,这个系统可以划分为挂号、门诊、划价、化验、收费、取药等。看病的病人要与这些部门打交道,就如同一个子系统的客户端与一个子系统的各个类打交道一样,不是一件容易的事情:首先病人必须先挂号,然后门诊;如果医生要求化验,病人必须首先划价,然后缴费,才可以到化验部门做化验;化验后再回到门诊室。如下图所示:
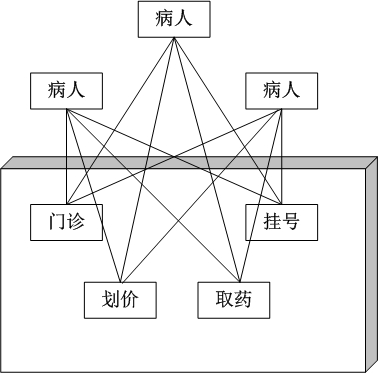
而如果引”进门面模式”,在医院中增加一个接待员。由接待员负责代为挂号、划价、缴费、取药等,病人只接触接待员,由接待员与各个部门打交道。这样,对病人来说,就会简单很多。如下图所示: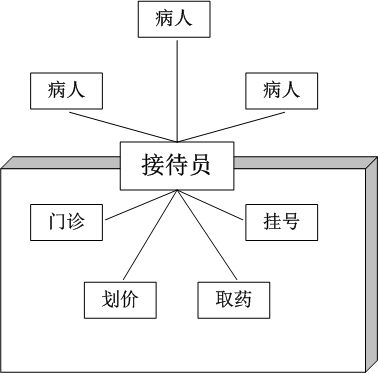
下面看看门面模式的UML类图: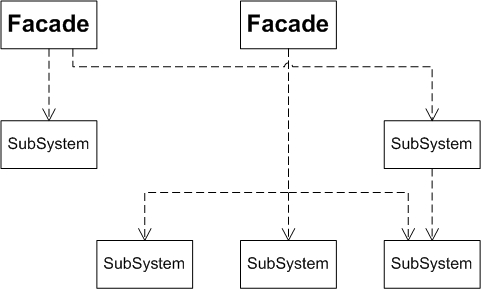
门面模式包括2个角色:门面(Facade),子系统(SubSystem)。
| 角色 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 门 面 | 客户端可以调用这个角色的方法。此角色知晓相关的(一个或者多个)子系统的功能和责任。在正常情况下,本角色会将所有从客户端发来的请求委派到相应的子系统去。 |
| 子系统 | 可以同时有一个或者多个子系统。每个子系统都不是一个单独的类,而是一个类的集合。每个子系统都可以被客户端直接调用,或者被门面角色调用。子系统并不知道门面的存在,对于子系统而言,门面仅仅是另外一个客户端而已。 |
门面模式示例
一个保安系统由两个录像机、三个电灯、一个遥控器和一个警报器组成。保安系统的操作人员在早上上班的时候,将这些仪器打开;晚上下班之后,会将这些仪器关闭。
我们先演示在不使用”门面模式”的情况下,实现该系统。然后,通过”门面模式”实现该系统。
未使用”门面模式”
UML类图如下: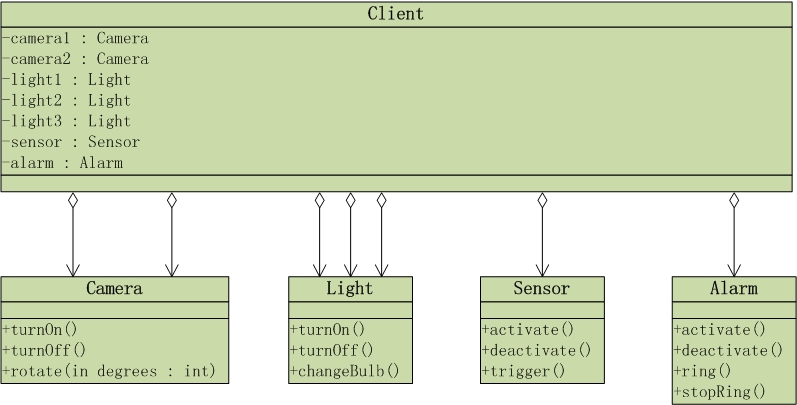
从图中可以看出,客户端Client对象需要引用到录像机(Camera)、电灯(Light)、感应器(Sensor)和报警器(Alarm)所有的对象。
客户端(Client)源码
public class Client {
private static Camera camera1, camera2;
private static Light light1, light2, light3;
private static Sensor sensor;
private static Alarm alarm;
public static void main(String[] args) {
camera1 = new Camera();
camera2 = new Camera();
light1 = new Light();
light2 = new Light();
light3 = new Light();
sensor = new Sensor();
alarm = new Alarm();
camera1.turnOn();
camera2.turnOn();
light1.turnOn();
light2.turnOn();
light3.turnOn();
sensor.activate();
alarm.activate();
}
}
录像机(Camera)源码
public class Camera {
// 打开录像机
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Turning on the camera.");
}
// 关闭录像机
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("Turning off the camera.");
}
// 转动录像机
public void rotate(int degrees) {
System.out.println("Rotating the camera by "+degrees+" degrees.");
}
}
电灯(Light)源码
public class Light {
// 打开灯
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Turning on the light.");
}
// 关闭灯
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("Turning off the light.");
}
// 换灯泡
public void changeBulb() {
System.out.println("Cotating the light-bulb.");
}
}
感应器(Sensor)源码
public class Sensor {
// 启动感应器
public void activate() {
System.out.println("Activating on the sensor.");
}
// 关闭感应器
public void deactivate() {
System.out.println("Deactivating the sensor.");
}
// 触发感应器
public void trigger() {
System.out.println("The sensor has been triggered.");
}
}
报警器(Alarm)源码
public class Alarm {
// 启动警报器
public void activate() {
System.out.println("Activating on the alarm.");
}
// 关闭警报器
public void deactivate() {
System.out.println("Deactivating the alarm.");
}
// 拉响警报器
public void ring() {
System.out.println("Ringing the alarm");
}
// 停掉警报器
public void stopRing() {
System.out.println("Stop the alarm");
}
}
运行结果:
Turning on the camera.
Turning on the camera.
Turning on the light.
Turning on the light.
Turning on the light.
Activating on the sensor.
Activating on the alarm.
使用”门面模式”
UML类图如下: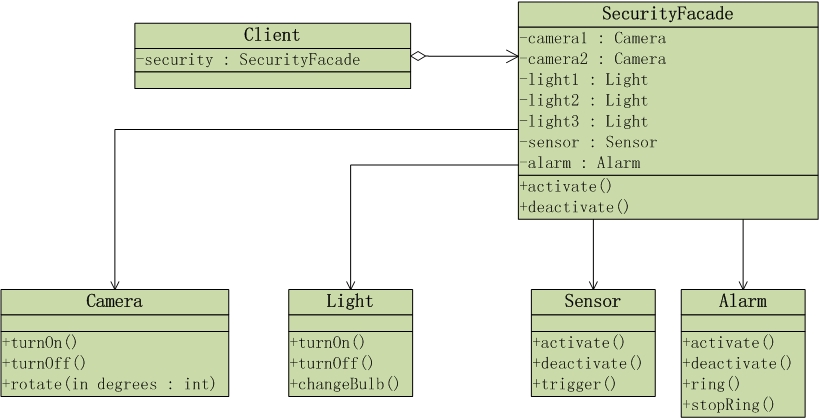
可以看出:门面SecurityFade承担了与保安系统内部各个对象打交道的任务,而客户对象只需要与门面对象打交道即可。SecurityFade是客户端与保安系统之间的一个门户,它使得客户端与子系统之间的关系变得简单和易于管理。
客户端(Client)源码
public class Client {
private static SecurityFacade security;
public static void main(String[] args) {
security = new SecurityFacade();
security.activate();
}
}
门面(SecurityFade)源码
public class SecurityFacade {
private Camera camera1, camera2;
private Light light1, light2, light3;
private Sensor sensor;
private Alarm alarm;
public SecurityFacade() {
camera1 = new Camera();
camera2 = new Camera();
light1 = new Light();
light2 = new Light();
light3 = new Light();
sensor = new Sensor();
alarm = new Alarm();
}
public void activate() {
camera1.turnOn();
camera2.turnOn();
light1.turnOn();
light2.turnOn();
light3.turnOn();
sensor.activate();
alarm.activate();
}
public void deactivate() {
camera1.turnOff();
camera2.turnOff();
light1.turnOff();
light2.turnOff();
light3.turnOff();
sensor.deactivate();
alarm.deactivate();
}
}
录像机(Camera)源码
public class Camera {
// 打开录像机
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Turning on the camera.");
}
// 关闭录像机
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("Turning off the camera.");
}
// 转动录像机
public void rotate(int degrees) {
System.out.println("Rotating the camera by "+degrees+" degrees.");
}
}
电灯(Light)源码
public class Light {
// 打开灯
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Turning on the light.");
}
// 关闭灯
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("Turning off the light.");
}
// 换灯泡
public void changeBulb() {
System.out.println("Cotating the light-bulb.");
}
}
感应器(Sensor)源码
public class Sensor {
// 启动感应器
public void activate() {
System.out.println("Activating on the sensor.");
}
// 关闭感应器
public void deactivate() {
System.out.println("Deactivating the sensor.");
}
// 触发感应器
public void trigger() {
System.out.println("The sensor has been triggered.");
}
}
报警器(Alarm)源码
public class Alarm {
// 启动警报器
public void activate() {
System.out.println("Activating on the alarm.");
}
// 关闭警报器
public void deactivate() {
System.out.println("Deactivating the alarm.");
}
// 拉响警报器
public void ring() {
System.out.println("Ringing the alarm");
}
// 停掉警报器
public void stopRing() {
System.out.println("Stop the alarm");
}
}
运行结果:
Turning on the camera.
Turning on the camera.
Turning on the light.
Turning on the light.
Turning on the light.
Activating on the sensor.
Activating on the alarm.


